GRhOOT Ontology
GRhOOT, the German RhetOrical OnTology, is a domain ontology of currently 110 rhetorical figures in the German language.
Here are the links to the ontology, the github repository, and a LODE documentation:
- Ontology in OWL format
- Github Repository
- HTML Documentation generated by LODE
- Paper: Kühn, R., Mitrović, J., & Granitzer, M. (2022): GRhOOT: Ontology of Rhetorical Figures in German. In Proceedings of The 13th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, June. European Language Resources Association. (to appear)
@InProceedings{kuehn2022ontology,
author = {Kühn, Ramona and Mitrović, Jelena and Granitzer, Michael},
title = ,
booktitle = {Proceedings of The 13th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference},
month = {June},
year = {2022},
address = {Marseille, France},
publisher = {European Language Resources Association},
notes = {to appear}
}
Goal
We developed a modular ontology of rhetorical figures. The formal representation shall facilitate their detection, thus improving sentiment analysis, argument mining, detecting hate speech/fake news, and many other tasks where non-literal language is important. The ontology can be a support for human annotators to create annotated datasets with rhetorical figures.
Methodology
Rhetorical figures can have a strong effect on the readers/listeners, but are often neglected in NLP. With our ontology, we want to tackle this problem and support the automatic detection and annotation of rhetorical figures. Our contributions are:
- Comparing each figure from the RetFig ontology if it exists in German.
- Together with German linguist and reference books, we evaluated if the properties are the same.
- Ontology modeled in Protégé for 110 rhetorical figures with names in English, Serbian, and example sentences.
- We modeled 36 additional figures.
- Completeness and Consistency Check: Competency questions answered by DL and SPARQL queries to ensure that the ontology works as expected.
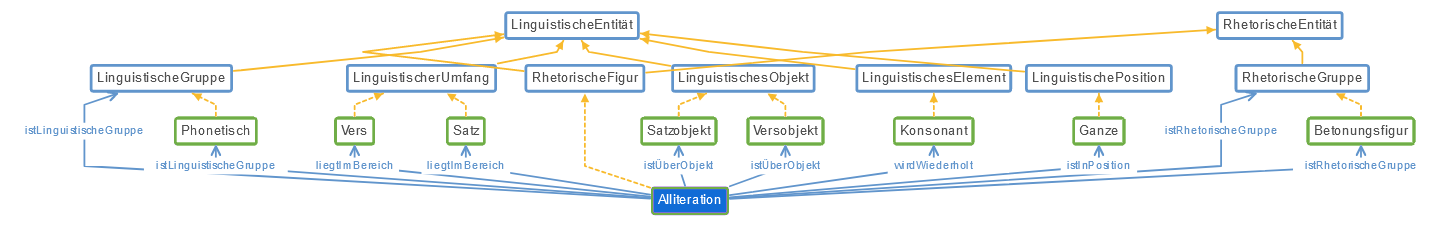
For example, the figure “Alliteration” looks like the following in the ontology:
Applications
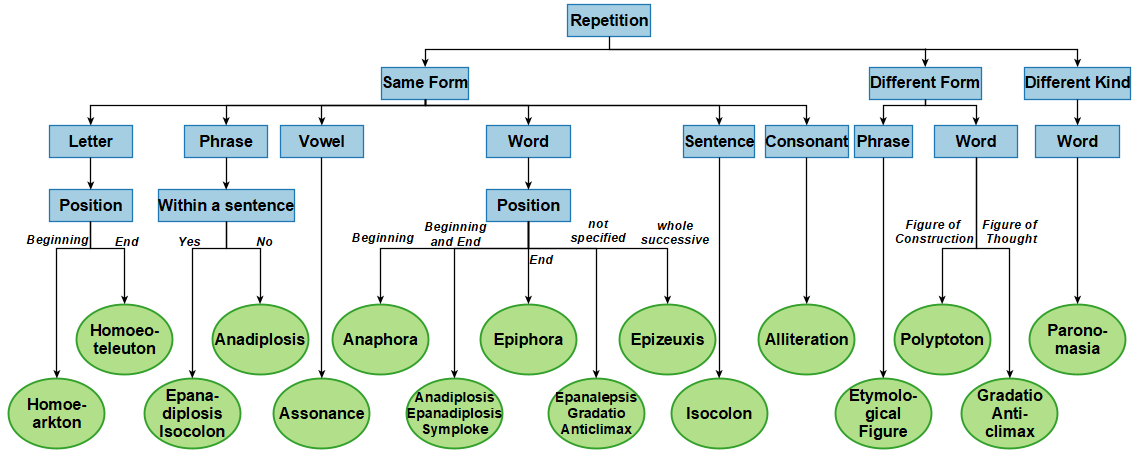
A decision tree based on the ontology can help to find the name for a figure: For example:
I like Salami Pizza! You like every Pizza!
Pizza:
(Repetition = yes) ∧ (SameForm = Word) ∧ (isInPosition = End) → Epiphora
like:
(Repetition = yes) ∧ (SameForm = Word) ∧ (isInPosition = notSpecified)
→ Epanalepsis/Gradatio/Anticlimax
We designed a decision tree for figures of repetition in GRhOOT:
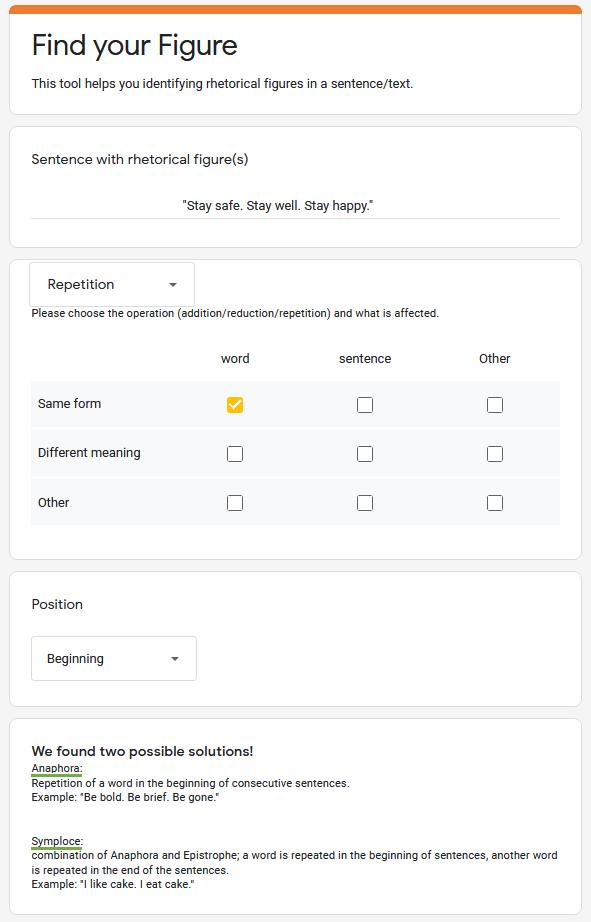
We are also planning to implement a web app that guides users interactively. User can choose text samples from the pool. An active learning approach helps at the annotation process, generating annotated data for machine learning models. Here is a draft of the UI:
Stay tuned for updates!